Chapter 8
Blood
8.2 Production of the Formed Elements
This section was edited and adapted from chapter 18.2 “Production of the Formed Elements” of the open source book Anatomy and Physiology 2e from OpenStax (original text available for free at https://openstax.org/details/books/anatomy-and-physiology-2e).
Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
-
Trace the generation of the formed elements of blood from bone marrow stem cells
-
Discuss the role of hemopoietic growth factors in promoting the production of the formed elements
The lifespan of the formed elements is very brief. Although one type of leukocyte called memory cells can survive for years, most erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets normally live only a few hours to a few weeks. Thus, the body must form new blood cells and platelets quickly and continuously. When you donate a unit of blood during a blood drive (approximately 475 mL, or about 1 pint), your body typically replaces the donated plasma within 24 hours, but it takes about 4 to 6 weeks to replace the blood cells. This restricts the frequency with which donors can contribute their blood. The process by which this replacement occurs is called hemopoiesis, or hematopoiesis (from the Greek root haima– = “blood”; –poiesis = “production”).
Sites of Hemopoiesis
Prior to birth, hemopoiesis occurs in a number of tissues, beginning with the yolk sac of the developing embryo, and continuing in the fetal liver, spleen, lymphatic tissue, and eventually the red bone marrow. Following birth, most hemopoiesis occurs in the red marrow, a connective tissue within the spaces of spongy (cancellous) bone tissue. In children, hemopoiesis can occur in the medullary cavity of long bones; in adults, the process is largely restricted to the cranial and pelvic bones, the vertebrae, the sternum, and the proximal epiphyses of the femur and humerus.
Throughout adulthood, the liver and spleen maintain their ability to generate the formed elements. This process is referred to as extramedullary hemopoiesis (meaning hemopoiesis outside the medullary cavity of adult bones). When a disease such as bone cancer destroys the bone marrow, causing hemopoiesis to fail, extramedullary hemopoiesis may be initiated.
Differentiation of Formed Elements from Stem Cells
All formed elements arise from stem cells of the red bone marrow. Recall that stem cells undergo mitosis plus cytokinesis (cellular division) to give rise to new daughter cells: One of these remains a stem cell and the other differentiates into one of any number of diverse cell types. Stem cells may be viewed as occupying a hierarchal system, with some loss of the ability to diversify at each step. The totipotent stem cell is the zygote, or fertilized egg. The totipotent (toti- = “all”) stem cell gives rise to all cells of the human body. The next level is the pluripotent stem cell, which gives rise to multiple types of cells of the body and some of the supporting fetal membranes. Beneath this level, the mesenchymal cell is a stem cell that develops only into types of connective tissue, including fibrous connective tissue, bone, cartilage, and blood, but not epithelium, muscle, and nervous tissue. One step lower on the hierarchy of stem cells is the hematopoietic stem cell, or hemocytoblast. All of the formed elements of blood originate from this specific type of cell.
Hemopoiesis begins when the hematopoietic stem cell is exposed to appropriate chemical stimuli collectively called hemopoietic growth factors, which prompt it to divide and differentiate. One daughter cell remains a hematopoietic stem cell, allowing hemopoiesis to continue. The other daughter cell becomes either of two types of more specialized stem cells (Figure 8.3):
-
Lymphoid stem cells give rise to a class of leukocytes known as lymphocytes, which include the various T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, all of which function in immunity. However, hemopoiesis of lymphocytes progresses somewhat differently from the process for the other formed elements. In brief, lymphoid stem cells quickly migrate from the bone marrow to lymphatic tissues, including the lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus, where their production and differentiation continues. B cells are so named since they mature in the bone marrow, while T cells mature in the thymus.
-
Myeloid stem cells give rise to all the other formed elements, including the erythrocytes; megakaryocytes that produce platelets; and a myeloblast lineage that gives rise to monocytes and three forms of granular leukocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
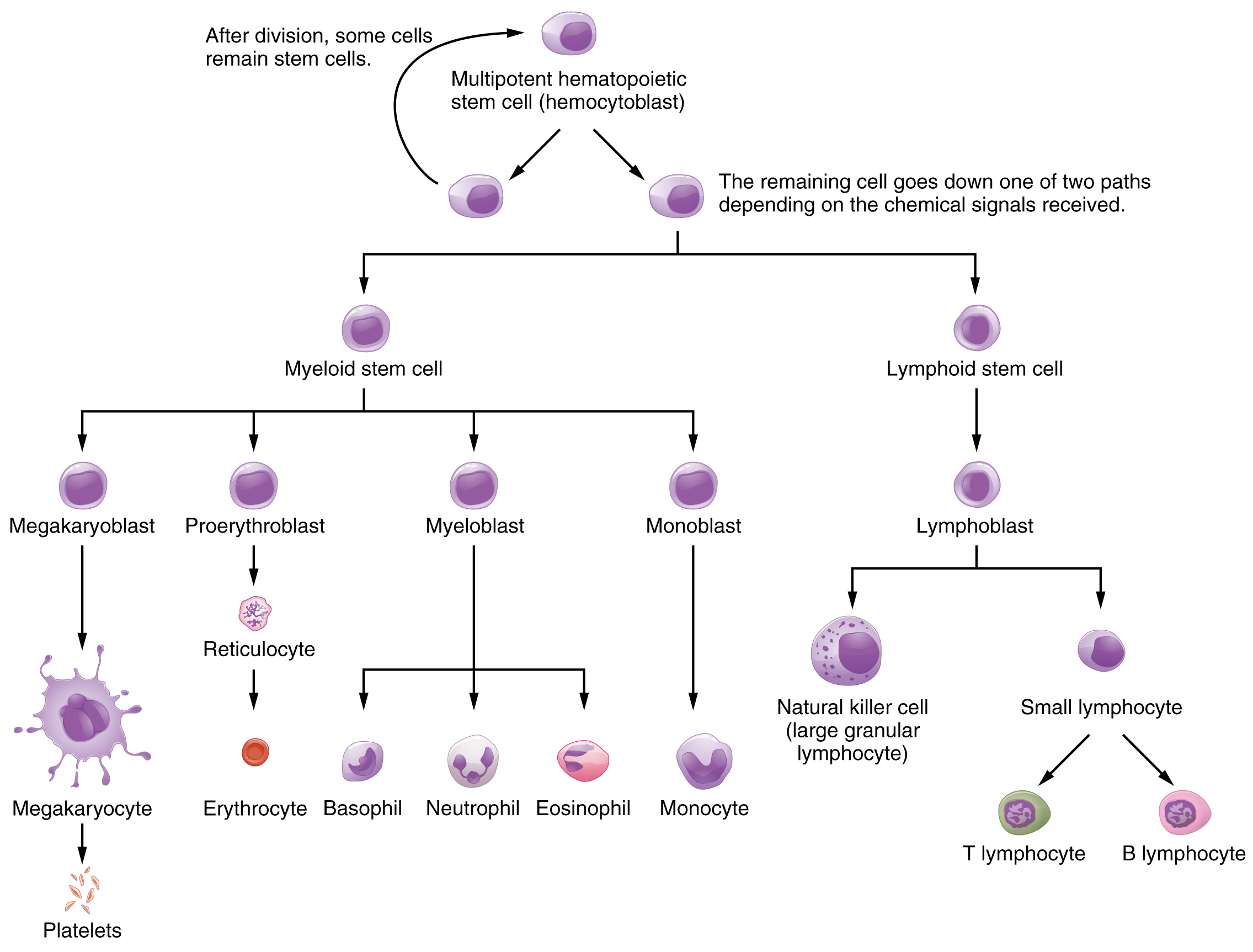
Lymphoid and myeloid stem cells do not immediately divide and differentiate into mature formed elements. As you can see in Figure 8.3, there are several intermediate stages of precursor cells (literally, forerunner cells), many of which can be recognized by their names, which have the suffix -blast. For instance, megakaryoblasts are the precursors of megakaryocytes, and proerythroblasts become reticulocytes, which eject their nucleus and most other organelles before maturing into erythrocytes.
Hemopoietic Growth Factors
Development from stem cells to precursor cells to mature cells is again initiated by hemopoietic growth factors. These include the following:
-
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a glycoprotein hormone secreted by the interstitial fibroblast cells of the kidneys in response to low oxygen levels. It prompts the production of erythrocytes. Some athletes use synthetic EPO as a performance-enhancing drug (called blood doping) to increase RBC counts and subsequently increase oxygen delivery to tissues throughout the body. EPO is a banned substance in most organized sports, but it is also used medically in the treatment of certain anemia, specifically those triggered by certain types of cancer, and other disorders in which increased erythrocyte counts and oxygen levels are desirable.
-
Thrombopoietin, another glycoprotein hormone, is produced by the liver and kidneys. It triggers the development of megakaryocytes into platelets.
-
Cytokines are glycoproteins secreted by a wide variety of cells, including red bone marrow, leukocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. They act locally as autocrine or paracrine factors, stimulating the proliferation of progenitor cells and helping to stimulate both nonspecific and specific resistance to disease. There are two major subtypes of cytokines known as colony-stimulating factors and interleukins.
-
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) are glycoproteins that act locally, as autocrine or paracrine factors. Some trigger the differentiation of myeloblasts into granular leukocytes, namely, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. These are referred to as granulocyte CSFs. A different CSF induces the production of monocytes, called monocyte CSFs. Both granulocytes and monocytes are stimulated by GM-CSF; granulocytes, monocytes, platelets, and erythrocytes are stimulated by multi-CSF. Synthetic forms of these hormones are often administered to patients with various forms of cancer who are receiving chemotherapy to revive their WBC counts.
-
Interleukins are another class of cytokine signaling molecules important in hemopoiesis. They were initially thought to be secreted uniquely by leukocytes and to communicate only with other leukocytes, and were named accordingly, but are now known to be produced by a variety of cells including bone marrow and endothelium. Researchers now suspect that interleukins may play other roles in body functioning, including differentiation and maturation of cells, producing immunity and inflammation. To date, more than a dozen interleukins have been identified, with others likely to follow. They are generally numbered IL-1, IL-2, IL-3, etc.
-
Everyday Connection
Blood Doping
In its original intent, the term blood doping was used to describe the practice of injecting by transfusion supplemental RBCs into an individual, typically to enhance performance in a sport. Additional RBCs would deliver more oxygen to the tissues, providing extra aerobic capacity, clinically referred to as VO2 max. The source of the cells was either from the recipient (autologous) or from a donor with compatible blood (homologous). This practice was aided by the well-developed techniques of harvesting, concentrating, and freezing of the RBCs that could be later thawed and injected, yet still retain their functionality. These practices are considered illegal in virtually all sports and run the risk of infection, significantly increasing the viscosity of the blood and the potential for transmission of blood-borne pathogens if the blood was collected from another individual.
With the development of synthetic EPO in the 1980s, it became possible to provide additional RBCs by artificially stimulating RBC production in the bone marrow. Originally developed to treat patients suffering from anemia, renal failure, or cancer treatment, large quantities of EPO can be generated by recombinant DNA technology. Synthetic EPO is injected under the skin and can increase hematocrit for many weeks. It may also induce polycythemia and raise hematocrit to 70 or greater. This increased viscosity raises the resistance of the blood and forces the heart to pump more powerfully; in extreme cases, it has resulted in death. Other drugs such as cobalt II chloride have been shown to increase natural EPO gene expression. Blood doping has become problematic in many sports, especially cycling. Lance Armstrong, winner of seven Tour de France and many other cycling titles, was stripped of his victories and admitted to blood doping in 2013.
Watch this video hosted on YouTube) to see doctors discuss the dangers of blood doping in sports.
What are the some potential side effects of blood doping?
Bone Marrow Sampling and Transplants
Sometimes, a healthcare provider will order a bone marrow biopsy, a diagnostic test of a sample of red bone marrow, or a bone marrow transplant, a treatment in which a donor’s healthy bone marrow — and its stem cells — replaces the faulty bone marrow of a patient. These tests and procedures are often used to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of various severe forms of anemia, such as thalassemia major and sickle cell anemia, as well as some types of cancer, specifically leukemia.
In the past, when a bone marrow sample or transplant was necessary, the procedure would have required inserting a large-bore needle into the region near the iliac crest of the pelvic bones (os coxae). This location was preferred, since its location close to the body surface makes it more accessible, and it is relatively isolated from most vital organs. Unfortunately, the procedure is quite painful.
Now, direct sampling of bone marrow can often be avoided. In many cases, stem cells can be isolated in just a few hours from a sample of a patient’s blood. The isolated stem cells are then grown in culture using the appropriate hemopoietic growth factors, and analyzed or sometimes frozen for later use.
For an individual requiring a transplant, a matching donor is essential to prevent the immune system from destroying the donor cells — a phenomenon known as tissue rejection. To treat patients with bone marrow transplants, it is first necessary to destroy the patient’s own diseased marrow through radiation and/or chemotherapy. Donor bone marrow stem cells are then intravenously infused. From the bloodstream, they establish themselves in the recipient’s bone marrow.
Section Review
Through the process of hemopoiesis, the formed elements of blood are continually produced, replacing the relatively short-lived erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets. Hemopoiesis begins in the red bone marrow, with hematopoietic stem cells that differentiate into myeloid and lymphoid lineages. Myeloid stem cells give rise to most of the formed elements. Lymphoid stem cells give rise only to the various lymphocytes designated as B and T cells, and NK cells. Hemopoietic growth factors, including erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, colony-stimulating factors, and interleukins, promote the proliferation and differentiation of formed elements.
Key Terms
- colony-stimulating factors (CSFs)
- glycoproteins that trigger the proliferation and differentiation of myeloblasts into granular leukocytes (basophils, neutrophils, and eosinophils)
- cytokines
- class of proteins that act as autocrine or paracrine signaling molecules; in the cardiovascular system, they stimulate the proliferation of progenitor cells and help to stimulate both nonspecific and specific resistance to disease
- erythropoietin (EPO)
- glycoprotein that triggers the bone marrow to produce RBCs; secreted by the kidney in response to low oxygen levels
- hematopoietic stem cell
- type of pluripotent stem cell that gives rise to the formed elements of blood (hemocytoblast)
- hemocytoblast
- hematopoietic stem cell that gives rise to the formed elements of blood
- hemopoiesis
- production of the formed elements of blood
- hemopoietic growth factors
- chemical signals including erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, colony-stimulating factors, and interleukins that regulate the differentiation and proliferation of particular blood progenitor cells
- interleukins
- signaling molecules that may function in hemopoiesis, inflammation, and specific immune responses
- lymphoid stem cells
- type of hematopoietic stem cells that gives rise to lymphocytes, including various T cells, B cells, and NK cells, all of which function in immunity
- myeloid stem cells
- type of hematopoietic stem cell that gives rise to some formed elements, including erythrocytes, megakaryocytes that produce platelets, and a myeloblast lineage that gives rise to monocytes and three forms of granular leukocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils)
- pluripotent stem cell
- stem cell that derives from totipotent stem cells and is capable of differentiating into many, but not all, cell types
- thrombopoietin
- hormone secreted by the liver and kidneys that prompts the development of megakaryocytes into thrombocytes (platelets)
- totipotent stem cell
- embryonic stem cell that is capable of differentiating into any and all cells of the body; enabling the full development of an organism
Review Questions
- Question 8.2.1
-
