Chapter 6
Skeletal System
6.1 Functions of the Skeletal System
Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
-
Define bone, cartilage, and the skeletal system
-
List and describe the functions of the skeletal system
Bone, or osseous tissue, is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton, the support structure of the body. In the areas of the skeleton where bones move (for example, the ribcage and joints), cartilage, a semi-rigid form of connective tissue, provides flexibility and smooth surfaces for movement. The skeletal system is the body system composed of bones and cartilage and performs the following critical functions for the human body:
-
supports the body
-
facilitates movement
-
protects internal organs
-
produces blood cells
-
stores and releases minerals and fat
Support, Movement, and Protection
The most apparent functions of the skeletal system are the gross functions — those visible by observation. Simply by looking at a person, you can see how the bones support, facilitate movement, and protect the human body.
Just as the steel beams of a building provide a scaffold to support its weight, the bones and cartilage of your skeletal system compose the scaffold that supports the rest of your body. Without the skeletal system, you would be a limp mass of organs, muscle, and skin.
Bones also facilitate movement by serving as points of attachment for your muscles. While some bones only serve as a support for the muscles, others also transmit the forces produced when your muscles contract. From a mechanical point of view, bones act as levers and joints serve as fulcrums (Figure 6.2). Unless a muscle spans a joint and contracts, a bone is not going to move. For information on the interaction of the skeletal and muscular systems, that is, the musculoskeletal system, seek additional content.

Bones also protect internal organs from injury by covering or surrounding them. For example, your ribs protect your lungs and heart, the bones of your vertebral column (spine) protect your spinal cord, and the bones of your cranium (skull) protect your brain (Figure 6.3).

Career Connection
Orthopedist
An orthopedist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders and injuries related to the musculoskeletal system. Some orthopedic problems can be treated with medications, exercises, braces, and other devices, but others may be best treated with surgery (Figure 6.4).
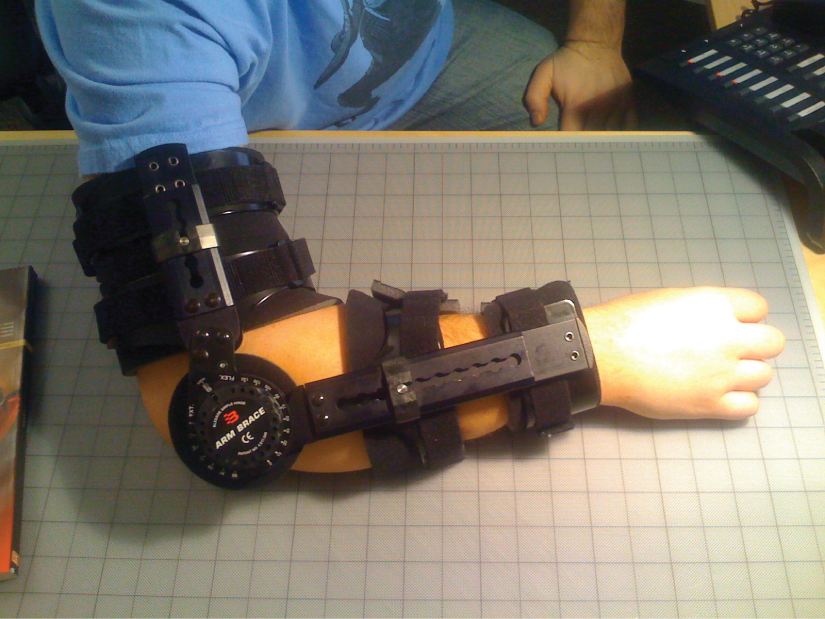
While the origin of the word “orthopedics” (ortho- = “straight”; paed- = “child”), literally means “straightening of the child,” orthopedists can have patients who range from pediatric to geriatric. In recent years, orthopedists have even performed prenatal surgery to correct spina bifida, a congenital defect in which the neural canal in the spine of the fetus fails to close completely during embryologic development.
Orthopedists commonly treat bone and joint injuries but they also treat other bone conditions including curvature of the spine. Lateral curvatures (scoliosis) can be severe enough to slip under the shoulder blade (scapula) forcing it up as a hump. Spinal curvatures can also be excessive dorsoventrally (kyphosis) causing a hunch back and thoracic compression. These curvatures often appear in preteens as the result of poor posture, abnormal growth, or indeterminate causes. Mostly, they are readily treated by orthopedists. As people age, accumulated spinal column injuries and diseases like osteoporosis can also lead to curvatures of the spine, hence the stooping you sometimes see in the elderly.
Some orthopedists sub-specialize in sports medicine, which addresses both simple injuries, such as a sprained ankle, and complex injuries, such as a torn rotator cuff in the shoulder. Treatment can range from exercise to surgery.
Mineral Storage, Energy Storage, and Hematopoiesis
On a metabolic level, bone tissue performs several critical functions. For one, the bone matrix acts as a reservoir for a number of minerals important to the functioning of the body, especially calcium, and potassium. These minerals, incorporated into bone tissue, can be released back into the bloodstream to maintain levels needed to support physiological processes. Calcium ions, for example, are essential for muscle contractions and controlling the flow of other ions involved in the transmission of nerve impulses.
Bone also serves as a site for fat storage and blood cell production. The softer connective tissue that fills the interior of most bone is referred to as bone marrow (Figure 6.5). There are two types of bone marrow: yellow marrow and red marrow. Yellow marrow contains adipose tissue; the triglycerides stored in the adipocytes of the tissue can serve as a source of energy. Red marrow is where hematopoiesis — the production of blood cells — takes place. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all produced in the red marrow.

Section Summary
The major functions of the bones are body support, facilitation of movement, protection of internal organs, storage of minerals and fat, and hematopoiesis. Together, the muscular system and skeletal system are known as the musculoskeletal system.
Key Terms
- cartilage
- semi-rigid connective tissue found on the skeleton in areas where flexibility and smooth surfaces support movement
- hematopoiesis
- production of blood cells, which occurs in the red marrow of the bones
- orthopedist
- doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders and injuries
- osseous tissue
- bone tissue; a hard, dense connective tissue that forms the structural elements of the skeleton
- red marrow
- connective tissue in the interior cavity of a bone where hematopoiesis takes place
- skeletal system
- organ system composed of bones and cartilage that provides for movement, support, and protection
- yellow marrow
- connective tissue in the interior cavity of a bone where fat is stored
Review Questions
- Question 6.1.1
-
- Question 6.1.2
-
- Question 6.1.3
-
- Question 6.1.4
-
- Question 6.1.5
-
- Question 6.1.6
-
- Question 6.1.7
-
